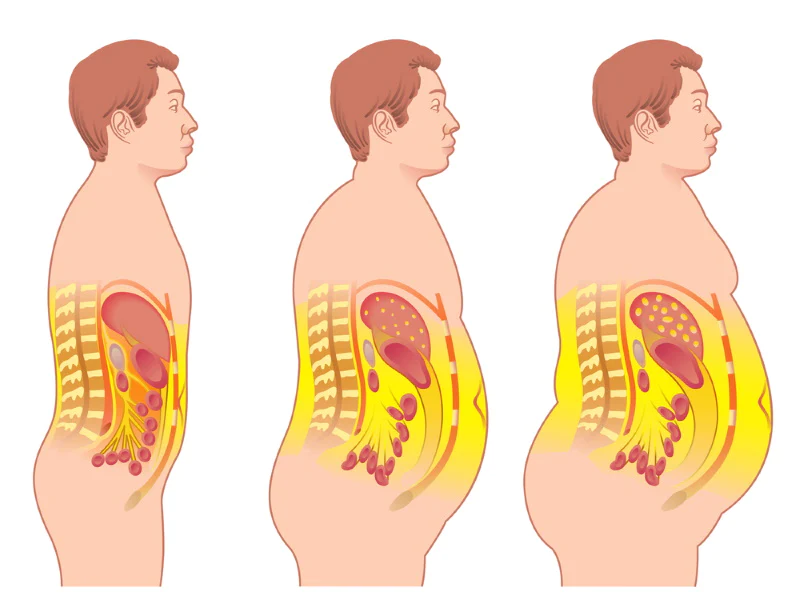
Visceral fat!
Visceral fat, also known as abdominal or intra-abdominal fat, is stored inside the abdominal cavity around vital organs such as the liver, pancreas, and intestines. This type of fat differs from subcutaneous fat, which is found under the skin and can also be found in organs and muscles.
Harmful health effects:
1) Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: Visceral fat cells are metabolically active and can release fatty acids and inflammatory agents. These substances can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
 2) Heart disease: Substances secreted by visceral fat can reach the liver, affecting blood lipid production. This can increase the risk of heart disease.
2) Heart disease: Substances secreted by visceral fat can reach the liver, affecting blood lipid production. This can increase the risk of heart disease.
3) Increased blood pressure: Visceral fat is linked to an increased risk of developing hypertension, a major risk factor for heart attack and stroke.
4) Inflammation and cancer: Visceral fat produces inflammatory substances that have been associated with an increased risk of certain cancers, including breast and colon cancer.
5) Hormonal imbalances: Visceral fat affects the production of hormones such as estrogen and the leptin, which can affect appetite, metabolism, and body weight regulation.
6) Impairment of cognitive function: Some studies suggest a link between visceral fat and reduced cognitive function, possibly due to inflammatory processes affecting brain health.
Management (reduction) of visceral fat: what can we do?
Diet: A diet low in carbohydrates, free of processed foods, rich in protein and healthy fats can help reduce visceral fat (the ketogenic/low carb diet is a good option).
Physical activity: Regular physical activity, particularly high-intensity workouts and strength training, can effectively reduce visceral fat.
Sleep: Adequate sleep is important for hormonal balance and can help manage body weight and fat distribution.
Stress management: High levels of stress can lead to an increase in cortisol, a hormone that can promote fat accumulation, particularly in the abdominal area.
Avoid alcohol: Excessive alcohol intake is linked to increased visceral fat. then, alas, even just one glass of wine in the evening blocks growth hormone, a very powerful lipolytic, for 24 hours
