by Oliver Ruatti
If proteins are the words with which the body writes its story-enzymes, hormones, receptors, muscles, skin-then amino acids are the letters of the alphabet with which these words are constructed.
And just as with any language, knowing the alphabet gives you the power to read, understand, optimize and even modify life itself.
There are only twenty amino acids, but from these twenty building blocks comes everything from muscle structure, nerve transmission, immunity, metabolism, and mood.
1. The Basics to Know
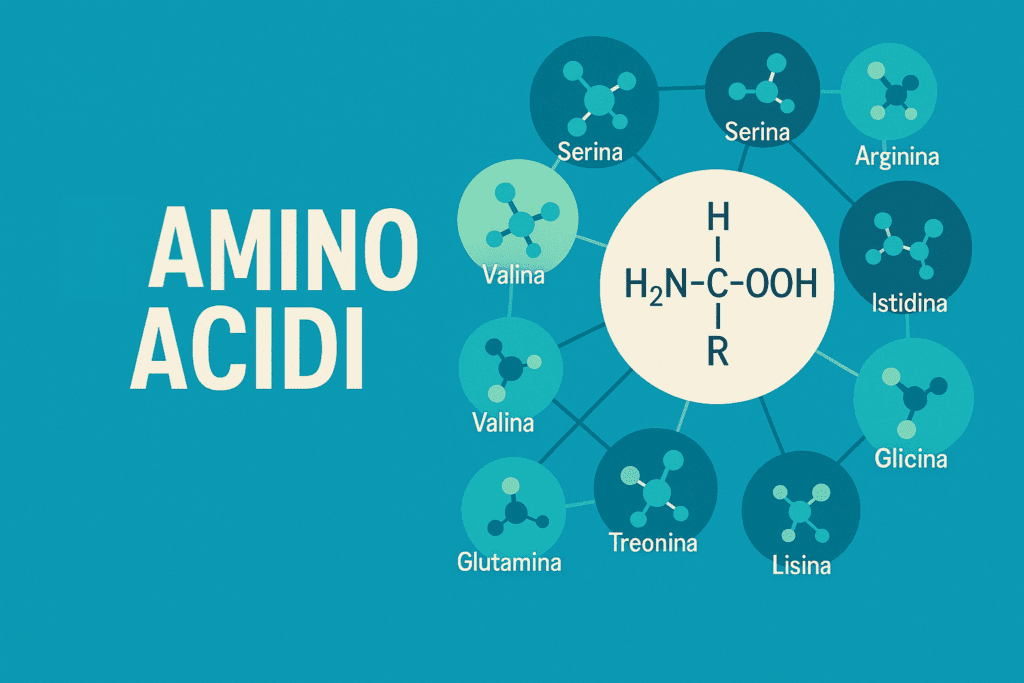
Each amino acid is a small molecule made with a common skeleton:
- an amine group (-NH₂),
- a carboxyl group (-COOH) and
- A central carbon atom.
But what makes it unique is the side group (also called side chain), which determines its chemical and biological personality.
Each amino acid has a name
(such as leucine), but also a 3-letter abbreviated code (e.g., Leu) and a 1-letter one (e.g., L for Leucine) to further abbreviate.
This is because, in our DNA, proteins are written as very long "words" composed of these letters.
A protein like hemoglobin, for example, is a chain of more than 140 amino acids, each represented by a letter: like a word that tells a precise function: transporting oxygen.
Example with oxytocin:
- It is a hormone composed of 9 amino acids.
- 3-letter code: Cys - Tyr - Ile - Gln - Asn - Cys - Pro - Leu - Gly
- 1-letter code: CYIQNCPLG
(Because some amino acids have identical initial letters, they are sometimes encoded by letters that have nothing to do with the name. Ex:
- Leucine=Leu=L;
- Lysine=Lys=K, since L encodes Leucine)
Oxytocin regulates functions such as:
- social bond
- uterine contraction and lactation
- relaxation, empathy, sense of connection
Each letter represents an amino acid. Changing even one can mean completely losing the biological function of the molecule.
2. Chemical Classes: Each Amino Acid Has a "Character."
Amino acids behave differently depending on the chemistry of their side group. We can group them into functional categories:
🔴 Aliphatics (hydrophobic)
Alanine, Glycine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine → They escape water. They are critical in stabilizing the inner "core" of proteins, contributing to the three-dimensional structure.
🟢 Aromatics
Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Tyrosine→ Contain aromatic rings capable of absorbing ultraviolet light. They participate in protein folding and specific interactions.
🟠 Acidic (negatively charged)
Aspartate (aspartic acid), Glutamate (glutamic acid)→ Negatively charged at physiological pH. Often found in the active sites of enzymes, where they catalyze vital reactions.
🔵 Basics (positive charge)
Lysine, Arginine, Histidine→ Positively charged. They are involved in DNA binding and gene regulation. Histidine, in particular, plays a key role in enzyme active sites.
💗 With hydroxyl groups
Serine, Threonine→ They contain an -OH group. They are often phosphorylated, that is, modified in response to cellular signals (signaling).
🟡 With sulfur
Cysteine, Methionine→ Cysteine can form disulfide bridges, actual molecular "hooks" that hold proteins together. Methionine is often the first amino acid from which a protein is built.
🔷 Amides (polar but neutral)
Asparagine, Glutamine→ They have no charge, but they are polar: excellent at creating hydrogen bonds, which help the protein interact with its environment.
Example: cysteine acts like a piece of Velcro: it can "glue" two parts of a protein together, making it more stable and strong.
3. Essential Amino Acids: The Ones You Need to Eat.
Among the 20 amino acids, 8 are essential for the human adult.
This means that we cannot synthesize them on our own: we have to take them in through diet.
Essential amino acids:
- Leucine
- Isoleucine
- Valina
- Lysine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
Some consider Histidine to be essential: it is in children; in adults it becomes a conditionally essential amino acid in these situations: Acute or chronic infections, trauma, surgery or burns, chronic inflammatory diseases, intense or prolonged physical activity, anemia or increased red blood cell production, chronic stress or mental fatigue, hypoprotein or vegetarian diets, prolonged fasting or severe caloric restriction, aging, high oxidative stress conditions.
These amino acids are found in optimal amounts in complete animal protein sources (such as eggs, meat, fish), but can also be combined from plant sources, albeit these with lower biological value.
Example: tryptophan is essential because it is used to produce serotonin, the neurotransmitter of good mood. If you don't get it with food, you can't produce serotonin-and your mental balance suffers.
One mistake can change everything
Hemoglobin is a protein consisting of four chains: two alpha and two beta chains. Each beta chain is 146 amino acids long.
In sickle cell anemia, a point mutation occurs in the sixth position of the beta chain:
👉 instead of glutamic acid (negatively charged and hydrophilic), a valine (nonpolar, hydrophobic) is inserted.
This small mistake, just one "wrong letter "in the protein code causes a structural catastrophe: the mutated hemoglobins tend to aggregate with each other, deforming the red blood cell into a "sickle" shape.
The result?
Stiff red blood cells, which get stuck in capillaries, reduce oxygenation, cause pain, ischemia, and permanent organ damage.
📌 One amino acid changed.
📌 One wrong letter out of 146.
📌 A life-saving cell becomes life-threatening.
20 Letters to Write l'Human
Biology created life with an alphabet of 20 amino acids.
Yet with so little, he wrote enzymes, hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, muscles, skin, hair, thoughts.
Understanding amino acids is not just a matter of biochemistry: it is learning to read the grammar you are made with.
The next time you eat a steak, an egg, or a handful of MAP, remember: you're not just feeding your muscles.
You are supplying your body with the letters with which it can continue to write your story.

MAP - L'Perfect protein supplement: pure, essential, brilliant
Imagine being able to take in only the amino acids your body really needs: in the perfect form, in the optimal ratio, and with near 100% bioavailability, producing almost no nitrogenous waste.
This is not a futuristic dream-it is the biochemical reality of MAPs (Master Amino Acid Patterns).
What it is the MAP?
MAP is a patented formula composed exclusively of the 8 essential amino acids in an exact ratio for the human body, in a pure, crystalline form.
It contains no fat, no sugar, and is not a "whole" protein-it is the purest, most direct, and most metabolic form of supplying the body with the basic building blocks of tissue, hair, enzymes, hormones, and muscle.
What makes MAPs so special?
- Immediate absorption
- MAP amino acids are absorbed within 23 minutes, directly through the intestinal mucosa, without requiring digestion.
- They do not overload the liver, kidneys or pancreas because they do not have agitated catabolites i.e., waste products.
- Zero waste
- When you take in "normal" protein (meat, eggs, whey...), only a portion is actually used. The rest is converted into urea, uric acid or glucose.
- MAPs, on the other hand, have a net utilization efficiency (NNU) of 99%. This means that virtually everything is used to build proteins and regenerate tissues, without burdening the
- Human amino acid profile
- The ratio of amino acids in MAPs has been studied to exactly replicate human requirements.
- No excess, no deficiency. Just what is needed, in the precise amount.
- Minimum calories, maximum impact
- Each tablet provides less than 0.5 kcal.
- 10 MAP = about 4 kcal, but with a surprisingly powerful anabolic and regenerative effect.
👉 This makes them perfect in dieting, fasting, or body recomposition strategies.
- Comparable to 100-120g of dietary protein, but...
- In terms of actual usable amino acids, 10 MAP can be equivalent to more than 300 g of meat or fish, but:
- fat-free
- without significant calories
- dross-free
- without digestive stress
Who can benefit from it?
- Athletes who want to maximize protein synthesis and muscle performance without burdening digestion.
- People undergoing fasting, detox, or illness who need nutrition without metabolic load.
- Biohackers, seniors, students, or anyone who wants to give the body the foundation to regenerate at its best.
- Chiunqe to optimize protein intake and cover protein requirements
MAP = Molecular intelligence
MAPs are not just a supplement: they are a language.
A language made of essential amino acids, in perfect syntax, to tell the body:
"Build, repair, regenerate, without waste."
If amino acids are the letters of the alphabet of life...
MAPs are like a molecular poem written without errors, ready to be transformed into enzymes, muscles, neurotransmitters, hormones, hair, and tissues.
Take advantage of MAP's 12-pack discount starting today, Oct. 18 and going through Oct. 28 inclusive!
CLICK HERE!

Great product I have been using it for more than 3 years ... I would like to understand how much protein is one map tablet.
Good morning, I am a 39-year-old woman with two children, weigh 53 kg and do water aerobics 2 times a week.
I eat pretty well despite the pace of work so I was interested for this to supplement what I lack in nutrition. Can I take how many maps a day without fear of overloading?
Thank you
Dr. Cristina ,explained
In an understandable way
I wanted to ask you in my case I am taking letrozole.
It could be useful
Making a course of treatment
To help me,or replace
bisphosphonates.
Did it reduce the pains?
Thank you
good morning, are there any powdered maps ?
do not exist, but you can put them in the blender and pulverize them you
Thank you for this valuable information.
For map intake, is it recommended away from meals? Is it better to possibly take it at a distance from taking magnesium? I imagine taking map after workout ending at 9 pm ..... then taking magnesium after dinner and before bedtime (around 11 pm) is it still recommended to take map away from magnesium?
Thank you very much Oliver for your valuable postings!!!
Before I met you and Cristina I was very skeptical about taking amino acids, I tried about 10 years ago but after taking them I regularly found it too difficult to digest them, whereas, since a few months ago, I tried MAPs and I said to myself geez but why didn't I try them as soon as I started following you and that is almost 2 years ago !!!
They are outstanding: no digestive difficulties at all, energy a go go, top skin and hair, and most importantly I reach the recommended amount of protein daily!!! Outstanding!!!
A hug
I'm really pleased dear Marina!
We have also been hiring them all continuously now since 2013
Good morning, Dr. Tomasi,
What is the dose to take, and for how long?
Thank you
Graziana
I have been taking MAP every day since 2013, at least 20 tablets a day.
A minimum of 10 I always recommend
In case of severe renal failure, grade 4, still not on dialysis, can Map be used?
absolutely yes, the characteristic of MAP is that it goes into protein synthesis at 99%, which means there are no nitrogen catabolites that overload kidneys and/or liver
Good morning, in a nutshell what are they for! Thank you
I wanted to know what they affect
Hi Dr. Tomasi, I wanted to ask you, can you take MAPs even if you take the recommended protein, 2 grams per body kilogram from eggs meat fish?
By doing physical activity of course,
Thank you in advance,
Best regards
Dear Julian,
If it already covers protein requirements completely, MAPs may be unnecessary
Thank you for the information and the clarity with which the topic was covered.
I would love to receive more insights into the essential components, which contribute to the functionality and well-being of our bodies.
Sincerely,
Cristina
Thank you Oliver, your writings are always very clear, simple and complete . You easily learn so many things about our body. Thank you again
Thank you for covering this topic in great detail but also clarity making clear the importance of supplementation of these essential AAs. Congratulations!
I'm glad dear Federica
Doctor one information can I give the maps to my son he was diagnosed with familial congenital dyslipidemia and he has uric acid Altino and also homocysteine is at 21 can I help him to disinfect.....graxie
Good evening how to calculate the amount of map to take during the day? Thank you
Good morning doctor, I'm very interested in the topic. But before I take them I would like to understand how to know, or rather if there is a way to know if I cover my protein requirements correctly.
I would like to participate in the next softmap, by the doctor, in anticipation of that do you recommend that I make the purchase and take advantage of the discount? What expiration dates do these products have? Thank you
Good morning I have been using MAPs for a few months and have gained 4.5 kg. Could it be the amino acids that have increased my body weight?
Thank you Doctor for the very accurate explanations
I got the maps.... Just one thing if I may ask.
Do you have to take the 10 tablets all at once or can they be divided into several administrations?
Thank you
Unfortunately, I am stationary with crutches due to knee lock due to meniscus fixation in multiple places. Prescribed physiotherapy and anti-inflammatories. Do I increase my intake of MAP? I take 10 a day. Thank you
Dear Doctor, I need one piece of information before purchasing Map. For the protein calculation, I would like to know how much protein you get from a 250 g steak.
I thank you in advance for your kind reply.
THANK YOU very much. Always very interesting all your valuable information.
I, too, have been taking MAP for about a year now, depending on how much other protein I take in through my diet.
I hope to be able to attend an in-person meeting Lake Garda area Verona
GOOD LIVING to all of you 🌞🌞🌞
Salve, giusto per fare un calcolo semplice, debbo considerare: 10 MAP circa 100 grammi di proteine?
Arrivano con l’acquisto le minime informazioni per l’assunzione?
Thank you
Salve, se riesco a coprire il mio fabbisogno proteico giornaliero, è necessario comunque assumere MAP? inoltre certe volte mi capita che la sera non ho fame, e li che devo assumere MAP? se si, quanti? grazie mille
Buongiorno
qual’è il dosaggio per ogni compressa?
l’obiettivo è di capire quante compresse al giorno è necessario prendere.
Thank you
Cordiali Saluti